Series: UML Mini-scenarios | Part 4 of 4 > Developed during Master’s in Web Systems Projects
We’ve reached the final scenario in this UML mini-scenarios series developed under the guidance of Professor Osmar Fernandes Jr. After exploring web classifieds , betting pool control , and construction control , we now model a parking system.
This final scenario demonstrates how UML can capture real-time operations, automatic calculations, and business rules based on time and context.
Scenario
When a vehicle enters the parking lot, the attendant records the license plate, car model, and color into the system.
The entry time is automatically generated at the moment of registration.
After parking, the customer receives a printed ticket showing:
- License plate number
- Vehicle model and color
- Entry date and time
Upon return, the customer hands over the ticket. The system calculates the length of stay and applies the correct pricing table, which may vary between weekdays and weekends.
The system also allows for special promotions, depending on the time of year.
Use Case Diagram
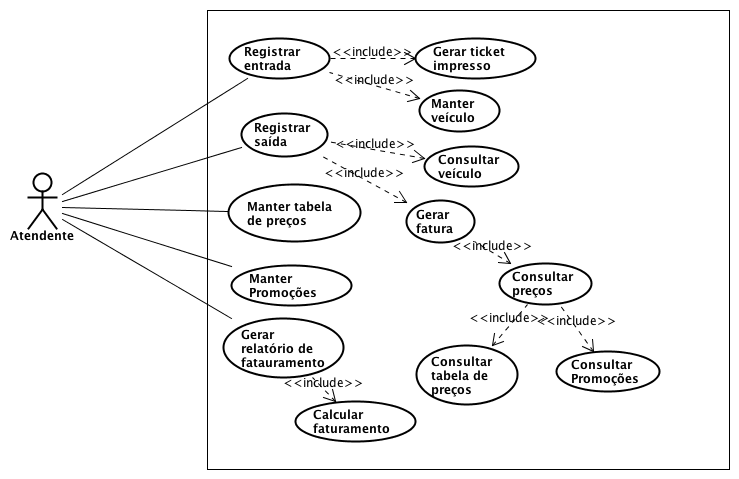
The Attendant is the primary actor and interacts with the system through the following actions:
- Register entry/exit: logs vehicle data and generates billing info.
- Maintain vehicle: updates or corrects vehicle information.
- Print ticket: given to the customer upon entry.
- Manage pricing table: configure different rates for weekdays and weekends.
- Manage promotions: add discounts based on specific periods.
- Calculate revenue: based on all registered activity.
- Generate billing report: for internal use.
Quick glossary:
- «include»: indicates one use case is always triggered as part of another (e.g., “Register entry” includes “Print ticket”).
- «extend»: represents optional behavior, conditionally executed (e.g., applying a promotion when generating an invoice).
Series Conclusion
This parking system concludes our UML mini-scenarios series, demonstrating how different business domains can be modeled with clarity and precision.
Throughout this series, we explored:
- Web Classifieds : System with multiple actors and automatic notifications
- Betting Pool Control : Financial management and participant control
- Construction Control : Price history and comparative reports
- Parking System: Real-time operations and automatic calculations
Each scenario illustrates different aspects of UML modeling, from simple use cases to complex relationships between classes and actors. UML use case modeling clearly outlines system responsibilities and interactions, regardless of the domain.
Series Navigation
- Introduction: Why UML Still Matters
- Previous: Part 3 - Construction Control
- Current: Part 4 - Parking System (Final)
- Complete series: Web Classifieds | Betting Pool Control | Construction Control